Mouse Interleukin 8 (IL-8/cxcl15) ELISA Kit
Regulatory status: For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedures.
2. Lyophilized Standard: 2 vial
3. Sample Dilution Buffer: 20 ml
4. Biotin-labeled Antibody (Concentrated): 120 μl
5. Antibody Dilution Buffer: 10 ml
6. HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate (SABC): 120 μl
7. SABC Dilution Buffer: 10 ml
8. TMB Substrate: 10 ml
9. Stop Solution: 10 ml
10. Wash Buffer (25×): 30 ml
11. Plate Sealer: 5 pieces
12. Product Description: 1 copy
Inter-Assay: CV < 10%
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
IL-8 belongs to the C-X-C subfamily (α subfamily), also known as chemokine CXCL8. The name IL-8 (interleukin-8)/NAP-1 is currently used in the literature. Chemokines (CK) are small molecule cytokines that can cause cells to undergo chemotaxis. Chemotaxis refers to the directional movement of cells toward high-concentration stimuli. According to the different arrangement and distribution of the first two of the four cysteine residues CYS in the highly conserved sequence at its N-terminus, it is divided into four categories: C, CC, CXC, and CX3C. IL8 is a protein with a very small molecular weight of about 8KD. Mature IL8 includes six forms: 79aa, 72aa, 71aa, 70aa and 69aa, of which 72aa is the main one. IL-8 of different molecular weights has different abilities to induce neutrophil chemotaxis and degranulation. IL-8 containing 72 amino acids has the strongest activity, which is usually referred to as mature IL-8. IL-8 can be divided into α and β subgroups. The gene of the α subgroup is located on chromosome 4, and the gene of the β subgroup is located on chromosome 17. It has been confirmed that IL1, PMA, and TNF can induce a variety of cells to express IL8mRNA, while IL-4 and glucocorticoids have an inhibitory effect on the expression of IL8. The main biological activity of IL8 is to attract and activate neutrophils. The secondary structure is composed of α helix and β sheet. Different specific proteases can decompose different parts of the N-terminus of the IL-8 precursor to produce IL-8 of different molecular weights. Among them, the IL-8 formed by protease cleavage in non-immune cells is a polypeptide containing 77 amino acids, while the IL-8 formed by enzyme cleavage in monocytes-macrophages is a polypeptide containing 72 amino acids. The human IL-8 gene is located on chromosome 4 (q12~q21). The IL-8 gene cloned from human placental genomic DNA is 5.2 kb in length and consists of 4 exons and 3 introns.
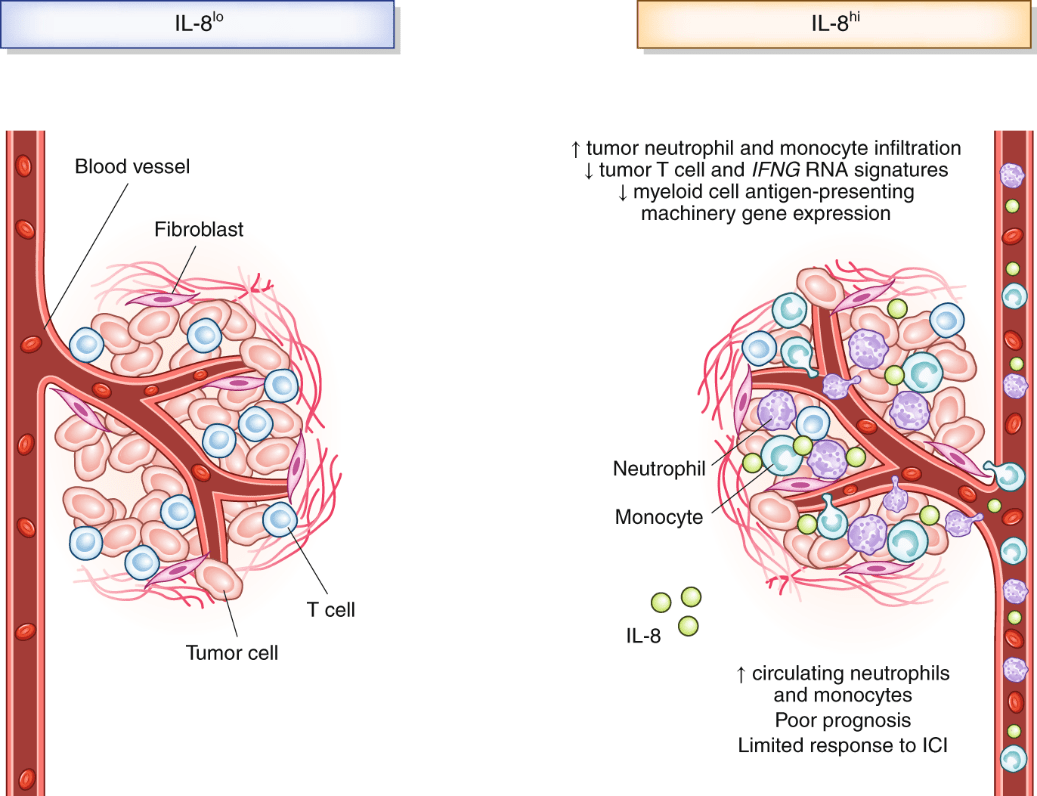 Figure 1. Production of IL-8 and effects on circulating immune cells, the tumor microenvironment and patient prognosis.(Sources: Bakouny Z, et al. 2020)
Figure 1. Production of IL-8 and effects on circulating immune cells, the tumor microenvironment and patient prognosis.(Sources: Bakouny Z, et al. 2020)
IL8 is involved in almost the entire reproductive process of mammals, such as ovulation, embryo implantation, and its growth and development. The main biological function of interleukin 8 is to chemotaxis neutrophils, T lymphocytes and basophils to the lesion site in the inflammatory response, and its chemotaxis is different for different cells. Neutrophils undergo morphological changes after contact with IL8, and they migrate to the reaction site in a directional manner and release a series of active products. These effects can lead to local inflammatory reactions in the body, achieving the purpose of sterilization and inflammatory damage. IL8 can make neutrophils express surface adhesion molecules, generate reactive oxygen metabolites, and cause a series of reactions such as tissue infiltration. IL8 has chemotaxis, activation, and degranulation effects on neutrophils. IL8 is mainly produced by mononuclear macrophages. In addition, other cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and hepatocytes can also produce IL-8 under appropriate stimulation conditions. Different biological activities have different names, such as monocyte-derived neutrophil chemoattractant factor (MDNCF), neutrophil activating factor (NAF), neutrophil activating peptide (NAP). The expression of interleukin 8 in cells is inducible. It requires the action of inducers such as IL1, TNFa, PHA (phytohemagglutinin-a mitogen, mainly used to activate immune cells) and LPS to synthesize and release a certain form of IL8. IL-8 receptor (IL-8R) is a dimeric glycoprotein. At present, there are at least two types of IL-8R known, namely CXCR1 (CXC receptor 1) and CXCR2 (CXCreceptor2), both of which belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family. It exists on the surface of many cells, among which the density of IL-8 receptor expressed by neutrophils is the highest, reaching 20,000 receptors/cell. Both receptors are transmembrane proteins, with the N-terminus located outside the cell and the C-terminus inside the cell, forming 7 transmembrane helical structures in the middle, including 3 extracellular loops and 3 intracellular loops, of which the C-terminus and the third intracellular loop are coupled to the G protein, while the N-terminus is the key region for IL-8R to recognize the ligand. Except for the N-terminus, the two IL-8Rs have a high homology (77%). CXCR1 specifically binds to IL8, and CXCR2 can bind to other chemokines such as GRO-a, GCP-2, ENA-78, etc. in addition to having a high affinity with IL8. Current studies have shown that in addition to endothelial cells, neutrophils, T cells and other tissue cells, a variety of tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages also have specific high expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2, suggesting that IL-8 may have a great impact on the tumor microenvironment.
CXCL1
KC
MGSA
Gro-alpha
References
1. Bakouny Z, Choueiri TK. IL-8 and cancer prognosis on immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2020, 26(5):650-651.
Changes in High-Density Lipoproteins Related to Outcomes in Patients with Acute Stroke
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MEDICINE
Authors: Varela, Lourdes M.; Meseguer, Elena; Lapergue, Bertrand; Couret, David; Amarenco, Pierre; Meilhac, Olivier
Association of SPOP Expression with the Immune Response to Salmonella Infection in Chickens
ANIMALS
Authors: Wang, Fei; Li, Qinghe; Wang, Qiao; Zheng, Maiqing; Wen, Jie; Zhao, Guiping
Invoice / Purchase Order
Credit card
![]()


