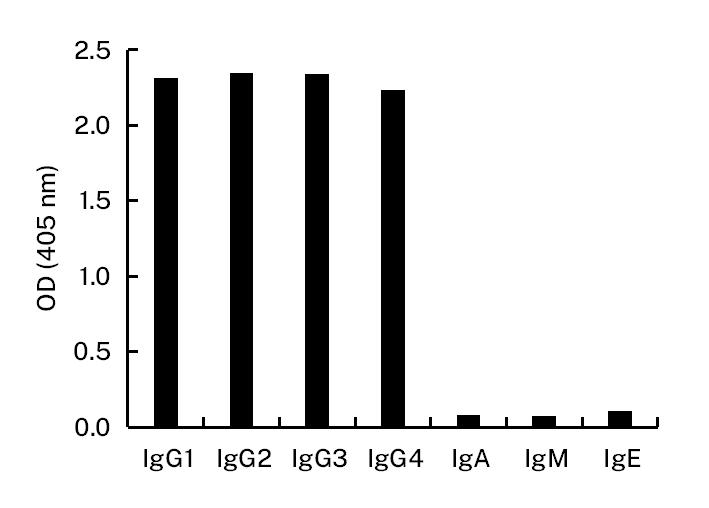
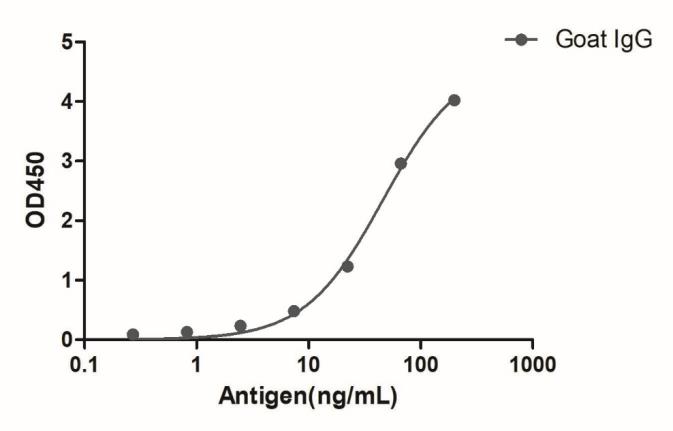
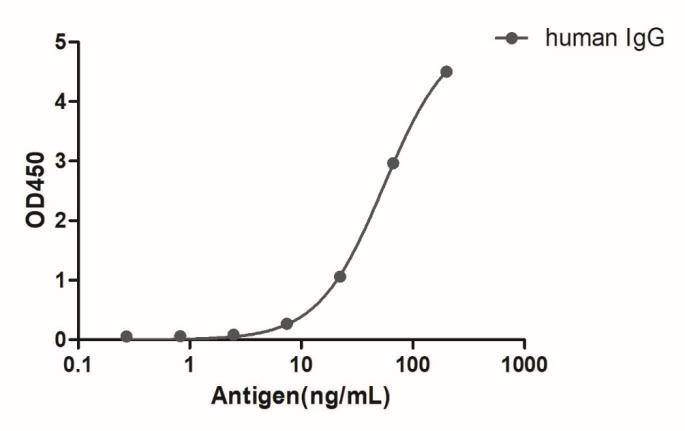
Recombinant Alpaca Anti-Rabbit IgG monoclonal antibody, Alexa Fluor®568
Alpaca Anti-Rabbit IgG monoclonal antibody, Alexa Fluor®568 for IF, WB, ELISA, recombinant VHH
Immunofluorescence 1:1,000
Super-resolution microscopy 1:1,000
Western blot 1:1,000
Optimal working concentration is application-dependent and should be determined by testing a dilution range from 1:250 to 1:2,000.
Note: Image acquisition time may have to be optimized.
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
Array-based analysis of SARS-CoV-2, other coronaviruses, and influenza antibodies in convalescent COVID-19 patients
BIOSENSORS & BIOELECTRONICS
Authors: Steiner, Daniel J.; Cognetti, John S.; Luta, Ethan P.; Klose, Alanna M.; Bucukovski, Joseph; Bryan, Michael R.; Schmuke, Jon J.; Nguyen-Contant, Phuong; Sangster, Mark Y.; Topham, David J.; Miller, Benjamin L.
Effect of whey protein isolate on the stability and antioxidant capacity of blueberry anthocyanins: A mechanistic and in vitro simulation study
FOOD CHEMISTRY
Authors: Zang, Zhihuan; Chou, Shurui; Tian, Jinlong; Lang, Yuxi; Shen, Yixiao; Ran, Xulong; Gao, Ningxuan; Li, Bin
Invoice / Purchase Order
Credit card
![]()
![HiResNb™ Anti-Goat IgG(Fcγ Fragment specific) VHH antibody, clone 165-212 [Biotin] (DMABB-JP05)](jpg/dmabb-jp05-1.jpg)
![HiResNb™ Anti-Goat IgG(Fcγ Fragment specific) VHH antibody, clone 165-212 [HRP] (DMABB-JP06)](jpg/dmabb-jp06-1.jpg)
![HiResNb™ Anti-Rabbit IgG VHH antibody, clone 21F21 [Atto 488] (DMABB-JP101)](jpg/dmabb-jp101_1.jpg)
![HiResNb™ Anti-Human IgG(Fcγ fragment specific) VHH antibody, clone 134-212 [Biotin] (DMABB-JP12)](jpg/dmabb-jp12-1.jpg)
![HiResNb™ Anti-Human IgG(Fcγ fragment specific) VHH antibody, clone 134-212 [HRP] (DMABB-JP13)](jpg/dmabb-jp13-1.jpg)