IHC/Pathology Antibodies
Creative Diagnostics offers a number of high quality pathology recombinant monoclonal antibodies including Her2, PD-1, Ki-67, Tim3, CTLA4, Lp-PLA2, Muc2, Cytokeratin 18, BRAF V600E, IDH1 R132H, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
View and select all our IHC/Pathology Antibodies:
CABT-L2806
HER2 monoclonal antibody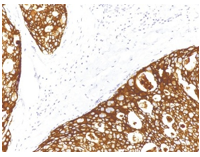
HER2:
This marker is identified in 10-20% of breast cancer patients. The Her2/Neu (c-erbB-2) proto-oncogene is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase that is clinically indicated in a number of carcinomas. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 protein has been associated with ductal breast cancer, as well as pulmonary and gastric adenocarcinomas.
A correlation between Her2 and p53 has also been documented, as overexpression of both proteins has been associated with early invasion and metastasis in bladder cancer.
CABT-L2883
FSH monoclonal antibody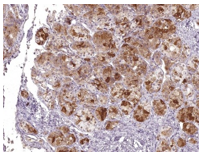
FSH:
FSH allows for progression of ovarian folliculogenesis, and enables Sertoli cell proliferation in the testis.
It is a hormone synthesized and secreted by gonadotropes in the anterior pituitary gland and is a useful marker in the classification of pituitary tumors and the study of pituitary disease.
CABT-L2813
Ki-67 monoclonal antibody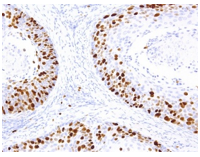
Ki-67:
Ki-67 is a nuclear non-histone protein that is present at low levels in quiescent cells but is increased in proliferating cells, especially in the G2, M, and latter half of the S phase.
Thus, Ki-67 reactivity, defined as percent tumor cells staining positive as measured by IHC staining, is a specific nuclear marker for cell proliferation. Overexpression is frequently seen in a variety of malignant tissues and associated with worse survival of individuals with a neuroendocrine tumor.
CABT-L2810
BRAF V600E monoclonal antibody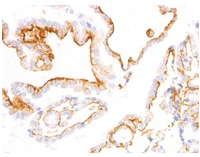
BRAF V600E:
BRAF is a cytoplasmic serine-threonine kinase of the RAF family which mediates downstream cellular responses to growth signals through the MAPK signaling pathway.
BRAF-V600E mutation are present in 57% of Langerhans cell histiocytosis patients. The V600E mutation is a likely driver mutation in 100% of cases of hairy cell leukemia. High frequency of BRAF V600E mutations have been detected in ameloblastoma, a benign but locally infiltrative odontogenic neoplasm.
PD-1: Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) is a member of the CD28/CTLA-4 family of T-cell regulators, expressed as a co-receptor on the surface of activated T-cells, B-cells, and macrophages. New studies have suggested that the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway may be linked to anti-tumor immunity, as PD-L1 has been shown to induce apoptosis of activated T cells or inhibit activity of cytotoxic T cells. Unlike CD10 and BCL6, PD-1 is expressed by few B-cells, so anti-PD-1 may be a more specific and useful diagnostic marker in angioimmunoblastic lymphoma.
CTLA4: The CD152 antigen, also called CTLA4, is an integral membrane protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, which is expressed either as a 30 kDa monomer or as a disulfide-linked homodimer. It has homology with the T cell antigen CD28, and like CD28, is a ligand for CD80 and CD86. CTLA-4 is a receptor on T Helper cells that functions as an immune checkpoint and down-regulator of immune responses. Mutations in CTLA-4 are associated many autoimmune diseases.
Lp-PLA2: Lp-PLA2, also known as Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2 or platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH), is an enzyme produced by inflammatory cells that functions to inactivate and degrade platelet-activating factor, a potent pro-inflammatory phospholipid, while also being responsible for hydrolyzing oxidatively modified polyunsaturated fatty acids. The products of the enzymatic actions of Lp-PLA2 have been linked to the development of atherosclerosis, and are positively correlated with increased risk of coronary heart disease and stroke.
Muc2: Mucin 2, also known as MUC2, is a human gene that encodes a member of the mucin protein family. The protein encoded by this gene forms an insoluble mucous barrier that protects the gut lumen. MUC2 expression is detected in human tissues such as normal colon, breast, prostate, and salivary gland, as well as in gastrointestinal, colonic, breast and prostate neoplasia.
Cytokeratin 18: Cytokeratin 18 (CK 18), a 45kDa protein, belongs to the acidic type of cytokeratins, and is typically expressed in simple, non-stratified epithelia. However, CK 18 is also expressed in basal and superficial cells of transitional epithelium, as well as in the luminal/secretory cells of complex epithelia. CK 18 antibody stains positively in Adenocarcinomas originating from simple and glandular epithelium, and also in poorly differentiated tumor cells of Squamous Carcinoma.
MLH1: MLH1, a mismatch repair protein involved in maintaining the integrity of genetic information, alongside MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2. This protein is commonly associated with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer, as the MLH1 gene is frequently mutated in patients with this cancer. Studies have shown MLH1 to be deficient in a high percentage of patients with microsatellite instability, as well as endometrial and ovarian cancers. Use of Anti-MLH1 is optimized when paired in an IHC panel with MSH6, MSH2, and PMS2.
Immunohistochemistry in molecular pathology plays three roles: Diagnosis, Prognosis and Predictive. IHC antibodies have been identified as the best reagents for use in immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed paraffin sections. Diagnostics implement quality control for immunohistochemistry staining methods and interpretation in pathology laboratories.
All the IHC/Pathology antibodies are for research use only. They have been extensively tested and validated for immunohistochemistry on human tissues and are engineered to deliver consistent, specific, and sensitive stains. Our IHC antibodies have been characterized at different concentrations against normal human or diseased tissues, plus additional relevant controls and are presented as prediluted format (Ready-to-use and optimized for staining) as well as concentrated format (Cost effective solution; can be optimized to meet the needs of each laboratory).
Please note that related Positive Control Slides are also available.
