Phospho-specific Antibodies
Creative Diagnostics offers extensive selection of phosphor-specific antibodies, which can be used in a variety of applications including Western blot, immunoprecipitations, immunofluorescence, FACS, ICC, and more.
- High-quality phospho-specific antibodies for more than 300 phosphoproteins or phosphorylation sites
- Custom special phospho-specific antibodies against every phosphoepitope of interest
- Available bulk quantities
- Well-established specification
- Guaranteed excellent services
Featured Phospho-specific Antibodies:
AKT/PDPK1
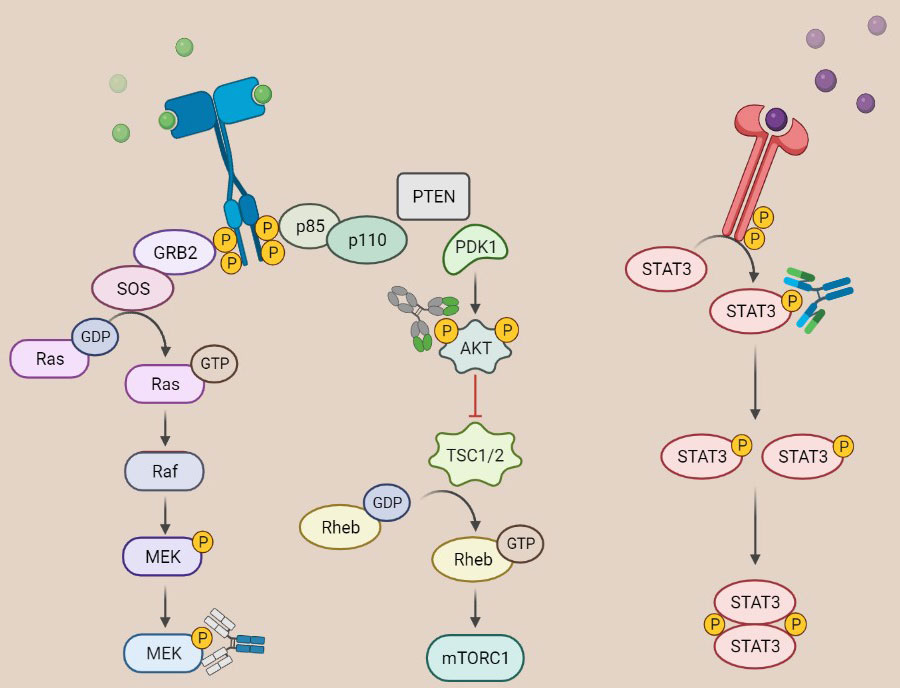
Akt, also named Protein Kinase B (PKB), is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, including the most important two, Akt1 and Akt2. The former one can inhibit apoptotic processes in cellular survival pathways and induce skeletal muscle hypertrophy and general tissue growth in cellular synthesis pathways, while the latter one is involved in the insulin signaling pathway. Akt can be phosphorylated by its activating kinase, phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1 (PDPK1), and phosphor-Akt plays an important role in glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription and cell migration.
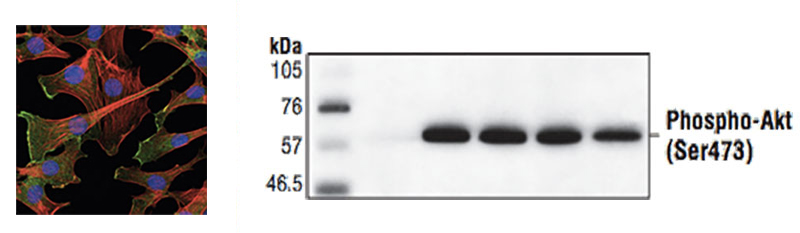 Magic™ Anti-AKT1 (Phospho S473) monoclonal antibody
Magic™ Anti-AKT1 (Phospho S473) monoclonal antibody
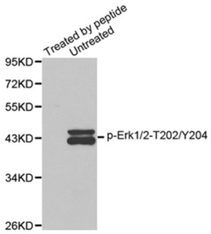
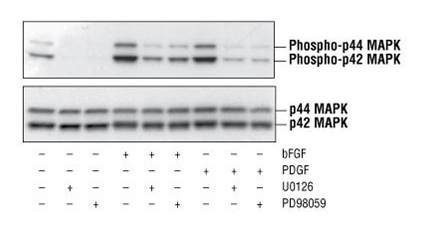
ERK/MAPK/MEK/ MAP2K
ERK/MAPK (extracellular signal–regulated kinases/Mitogen-activated protein kinase) is mainly involved in the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway regulating translation and transcription. Phosphorylation of ERKs leads to the activation of Raf/ERK /MEK cascade, including c-Raf activated by Ras and ERK/MAPK activated by MEK (MAPK/ERK kinase, also named MAP2K, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase) and then MAPK1/2. Aberrant activation of ERK/MAPK pathway leads to uncontrolled growth in most cancer, whose inhibitors, on the other hand, become considerable appeal as potential pharmacological treatments across a broad spectrum of cancers. Additionally, phospho-ERK can be applied in the common end point measurement for the activation of GPCR (G protein coupled receptors).
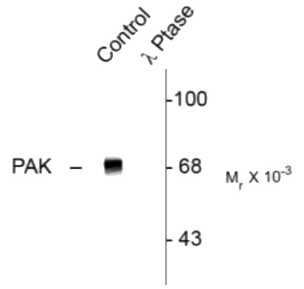
PAK
The PAKs (p21-activated kinases) are a serine/threonine kinases family with six isoforms (PAK1-6). They are the direct targets of the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42. PAKs prominently function as cytoskeletal dynamic regulator, as well as the pivotal role in cell survival, apoptosis, cell proliferation, mitosis, cell motility, and transcription. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation take part in the PAK activation loop. Involved in various oncogenic signaling pathways, PAKs has recently attracted more and more attention for the development of Pak inhibitors as anti-tumor therapeutics.
TAU
Tau are microtubules stabilizing proteins which are primarily expressed in neurons but rarely in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. Tau is able to promote tubulin assembly into microtubules and control microtubules stability by isoforms and phosphorylation. Tau currently constitutes a major focus for drug discovery due to its excessive or abnormal phosphorylation in pathologies and dementias of neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
STAT/JAK
STAT (the signal transducer and activator of transcription) is the protein family including STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5A and STAT5B and STAT6. They are primarily activated by Janus kinases (JAK) and involved in the JAK-STAT signalling cascade, which mediates immunity, proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation and oncogenesis, together with a cell surface receptor. Its dysregulation or disruption is related to primary tumors and immune deficiency.
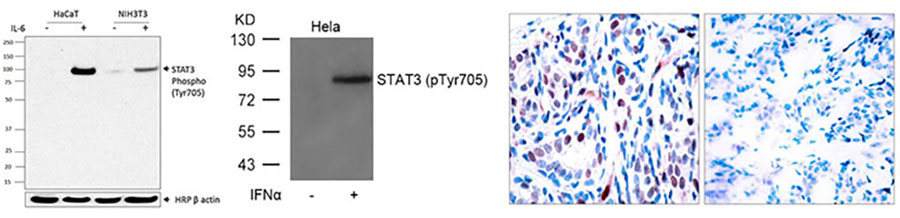 STAT3 (Phospho Y705) monoclonal antibody
STAT3 (Phospho Y705) monoclonal antibody
Phospho-specific antibodies, targeting at protein phosphorylation, are one of the recently well-developed and popularly-searched antibodies. Protein phosphorylation constitutes a key post-translational modification involved in regulation of cell signaling pathways governing a diversity of cellular processes via two mechanisms. One is to generate some new specific protein-binding sites and then lead to the formation of some functional proteins complexes. The other one is to induce conformational changes by phosphorylation at specific residues, which may result in altered enzymatic activity or ion channel permeability. There are three amino acids most commonly phosphorylated: Serine (S), Threonine (T) and Tyrosine (Y). It is critical to use phosphorylation specific antibodies in the study of protein phosphorylation in situ, which elucidates the role of phosphorylation events in producing complex biological effects. The development of phosphorylation specific antibodies makes it possible to reveal the pathology of some human diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, inflammation and endocrine disease. In addition, phosphotyrosine antibody, which specifically binds to phosphorylated tyrosine residues, is a valuable tool for analyzing tyrosine kinase activity in high-throughput drug discovery research.
With team of antibody experts working in a state-of-the-art laboratory, Creative Diagnostics provides various monoclonal and specific affinity-purified polyclonal phosphorylation specific antibodies with high sensitivity. All of our advanced instruments and well-developed protocols including peptides design, synthesis, screening strategies and antibody purification together, make it possible to produce a wide variety of phospho-specific antibodies against most phosphoepitope by synthesizing specific phosphopeptides with high purity and low cross reactivity with non-phospho peptide guaranteed.