Our range of vaccine R&D reagents include more than 40 native antigens of key infectious pathogens, including Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Clostridium tetani, Enterovirus, Hepatitis virus, Influenza virus, Poliovirus, Rotavirus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Zika virus. These antigens can be used in a variety of applications, from the development of conjugate vaccines, to the evaluation of vaccination efficacy by antibody tests.
Conjugate vaccines
Diphtheria and tetanus are two infectious diseases that are particularly dangerous to babies. Chemically detoxified bacterial toxins (toxoids) have been successfully used as vaccines for the prevention of diphtheria and tetanus, DT (diphtheria and tetanus) vaccine, Td (tetanus and diphtheria) vaccine and many other combination vaccines. Tetanus toxoid (TT), diphtheria toxoid (DT) and diphtheria CRM197 are also widely used as protein carriers in licensed vaccines (Hib, pneumococcal, and meningococcal) to develop strong immune responses. Conjugate vaccines rely on these immunogenic molecules to stimulate long-lasting immunity to attached polysaccharides or peptides.
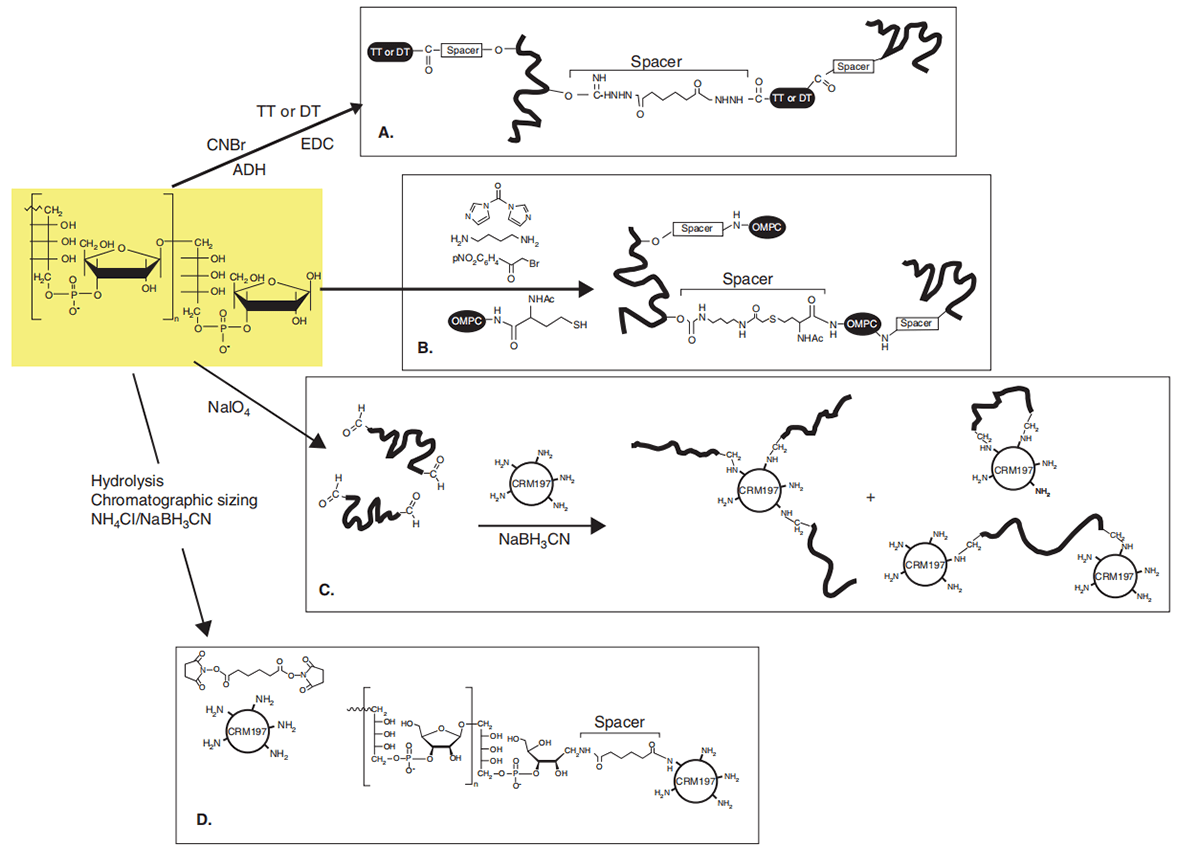 Fig. 1 Preparation processes of licensed Hib conjugate vaccines (Costantino P, et al. 2011)
Fig. 1 Preparation processes of licensed Hib conjugate vaccines (Costantino P, et al. 2011)
Pneumococcal vaccines
The capsular polysaccharide (CPS) is the dominant surface structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumoniae) and plays a critical role in defense against the host immune system. There are two polyvalent pneumococcal vaccines with CPS-based formulations approved for use in the United States: Prevnar13 (PCV13) and Pneumovax 23 (PPSV23). Prevnar13 is for adults 18 years of age and older by 13 S. pneumoniae serotypes (1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A,19F, and 23F), all of them are individually conjugated to a CRM197 protein. Pneumovax 23 is for adults 50 years of age or older and persons aged ≥2 years by 23 S. pneumoniae serotypes (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 8, 9N, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 17F, 18C, 19F, 19A, 20, 22F, 23F, and 33F). The detection of serotype-specific antibody levels in human sera is very important for differential diagnostics of pneumococcal infections and assessment of immunologic responses after pneumococcal vaccination.
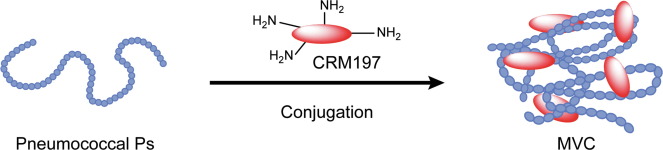 Fig. 2 Pneumococcal conjugation (Deng JZ, et al. 2022)
Fig. 2 Pneumococcal conjugation (Deng JZ, et al. 2022)
| Cat_N | Product Name |
| DAGC723 | S. pneumoniae Type 1 CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC724 | S. pneumoniae Type 3 CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC725 | S. pneumoniae Type 4 CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC726 | S. pneumoniae Type 5 CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC727 | S. pneumoniae Type 6A CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC728 | S. pneumoniae Type 6B CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC729 | S. pneumoniae Type 7F CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC730 | S. pneumoniae Type 9V CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC731 | S. pneumoniae Type 14 CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC732 | S. pneumoniae Type 18C CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC733 | S. pneumoniae Type 19A CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC734 | S. pneumoniae Type 19F CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| DAGC735 | S. pneumoniae Type 23F CPS-CRM197 conjugate |
| Cat_N | Product Name |
| DAGC700 | S. Pneumoniae Type 1 CPS |
| DAGC701 | S. pneumoniae Type 2 CPS |
| DAGC702 | S. pneumoniae Type 3 CPS |
| DAGC703 | S. pneumoniae Type 4 CPS |
| DAGC704 | S. pneumoniae Type 5 CPS |
| DAGC705 | S. pneumoniae Type 6B CPS |
| DAGC706 | S. pneumoniae Type 7F CPS |
| DAGC707 | S. pneumoniae Type 8 CPS |
| DAGC708 | S. pneumoniae Type 9N CPS |
| DAGC709 | S. pneumoniae Type 9V CPS |
| DAGC710 | S. pneumoniae Type 10A CPS |
| DAGC711 | S. pneumoniae Type 11A CPS |
| DAGC712 | S. pneumoniae Type 12F CPS |
| DAGC713 | S. pneumoniae Type 14 CPS |
| DAGC714 | S. pneumoniae Type 15B CPS |
| DAGC715 | S. pneumoniae Type 17F CPS |
| DAGC716 | S. pneumoniae Type 18C CPS |
| DAGC717 | S. pneumoniae Type 19A CPS |
| DAGC718 | S. pneumoniae Type 19F CPS |
| DAGC719 | S. pneumoniae Type 20 CPS |
| DAGC720 | S. pneumoniae Type 22F CPS |
| DAGC721 | S. pneumoniae Type 23F CPS |
| DAGC722 | S. pneumoniae Type 33F CPS |
Viral vaccines
There are few specific therapies for viral infections, vaccination is an effective way to prevent viral infections. Viral vaccines contain either inactivated viruses or attenuated (alive but not capable of causing disease) viruses. These viruses lost their ability to replicate and are not pathogenic but they can induce an immune response. To cause immune reaction, it contains more antigen than live vaccines. There are several licensed viral vaccines use in the US: Hepatitis A vaccine, Influenza virus vaccine, Poliovirus vaccine, and Rotavirus Vaccine. Currently, there are still many viral vaccines under pre-clinical and clinical stages.
References
- Costantino P, Rappuoli R, Berti F. (2011). The design of semi-synthetic and synthetic glycoconjugate vaccines. Expert Opinion Drug Discovery. 6(10), 1045-1066.
- Paton JC, Trappetti C. (2019). Streptococcus pneumoniae Capsular Polysaccharide. Microbiology Spectrum Journal Homepage. 7(2).
- Deng JZ, Lancaster C, Winters MA, et al. (2022). Multi-attribute characterization of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine by Size-exclusion chromatography coupled with UV-MALS-RI detections. Vaccine. 40(10), 1464-1471.
| Cat_N | Product Name | |
| DAG2692 | Tetanus Toxoid (TT) | Inquiry |
| DAG2689 | Diphtheria Toxoid (DT) | Inquiry |
| DADF-086 | Diphtheria CRM197 | Inquiry |
| DAGL0481 | Polyribosyl Ribitol Phosphate (PRP) | Inquiry |
| Cat_N | Product Name | |
| DAGC694 | Inactivated Coxsackievirus A16 | Inquiry |
| DAG-EV71 | Inactivated Enterovirus 71 Virus | Inquiry |
| DAG178 | Inactivated Hepatitis A Virus | Inquiry |
| DAG-WT664 | Inactivated IAV H1N1 | Inquiry |
| DAG-WT665 | Inactivated IAV H3N2 | Inquiry |
| DAG-WT666 | Inactivated IAV H5N1 | Inquiry |
| DAG-WT667 | Inactivated IAV H7N9 | Inquiry |
| DAG-WT668 | Inactivated IBV | Inquiry |
| DAGC457 | Inactivated Rotavirus | Inquiry |
| DAGC691 | Inactivated Sabin Poliovirus Type I | Inquiry |
| DAGC692 | Inactivated Sabin Poliovirus Type II | Inquiry |
| DAGC693 | Inactivated Sabin Poliovirus Type III | Inquiry |
| DAGC460 | Inactivated Zika Virus | Inquiry |