Host cell proteins (HCPs) constitute a major part of process-related impurities during recombinant biologics production. The amount of residual HCP in drug product is generally considered a critical quality attribute (CQA), due to their potential to affect the safety and efficacy of the drug. To ensure patient safety, it is a regulatory requirement to monitor the removal of HCPs in drug products during bioprocess development. Therefore, highly sensitive and robust tools are needed for reliable monitoring of the broad spectrum of which HCPs comprise. Currently, polyclonal antibodies are the most commonly used tool for detecting and monitoring HCPs due to the broad heterogeneity in the types of residual HCPs.
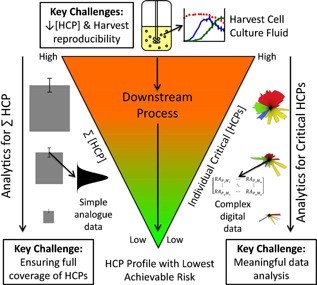 Fig. 1 Overview of the HCP landscape in the context of biologics manufacture (Bracewell et al., 2015)
Fig. 1 Overview of the HCP landscape in the context of biologics manufacture (Bracewell et al., 2015)
HCP in different host cells
The HCP mixture consists of a large number of protein species, which are unique to the specific host. Moreover, they can undergo post-translational modifications that make quantification and characterization more difficult. More than 70% of biological drug substances are produced using CHO cells, but Escherichia coli, Pichia pastoris, and HEK 293 cells are also common expression platforms. There is a range from 4,300 genes in E. coli to 30,000 genes in CHO or NS0 cell lines that may be expressed along with the desired recombinant product. Because these HCPs are potentially immunogenic, a commonly accepted method to evaluate the presence of HCPs is through an immunoassay. Regulatory requirements for the final product include the removal of host cell proteins (HCPs) to acceptable amounts (<100 ppm).
Immunoassays for Measuring and Monitoring Residual HCPs
To date, immunoassay, commonly in the form of sandwich ELISA assay, is a critical tool for monitoring purification process consistency as well as final drug substance purity and is the gold standard method for product monitoring and release testing accepted by authorities due to its high sensitivity and high throughput. HCP ELISA can measure ng/ml levels of HCP in the presence of mg/ml levels of product protein. The western blot method is commonly used to identify HCPs in drug substance samples and help to determine the HCP molecular scope in upstream harvest samples and provides predictive value in determining how the ELISA using the same antibody will quantitatively react to the more limited array of HCPs in downstream samples. It is also frequently used to determine the HCP antibody coverage when combined with 2D-DIGE.
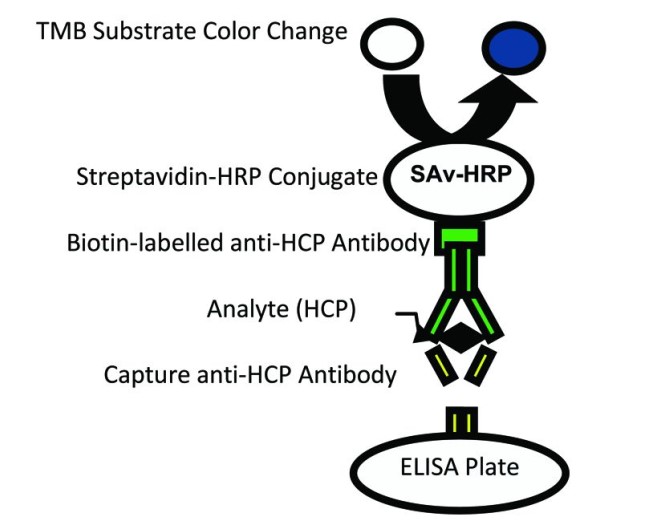 Fig.2 Sandwich ELISA for HCP detection. (Prakash and Chen, 2015)
Fig.2 Sandwich ELISA for HCP detection. (Prakash and Chen, 2015)
References
- Bracewell, D.G., Francis, R. and Smales, C.M., 2015. The future of host cell protein (HCP) identification during process development and manufacturing linked to a risk‐based management for their control. Biotechnology and bioengineering, 112(9), pp.1727-1737.
- Prakash, K. and Chen, W., 2015. Analytical methods for the measurement of host cell proteins and other process-related impurities. In State-of-the-Art and Emerging Technologies for Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibody CharacterizationVolume 2. Biopharmaceutical Characterization: The NISTmAb Case Study (pp. 387-404). American Chemical Society.
- Kendrick, N., Darie, C.C., Hoelter, M., Powers, G. and Johansen, J., 2019. 2D SDS PAGE in combination with Western blotting and mass spectrometry is a robust method for protein analysis with many applications. Advancements of Mass Spectrometry in Biomedical Research, pp.563-574.
- Park, J.H., Jin, J.H., Lim, M.S., An, H.J., Kim, J.W. and Lee, G.M., 2017. Proteomic analysis of host cell protein dynamics in the culture supernatants of antibody-producing CHO cells. Scientific reports, 7(1), p.44246.
| Cat No. | Product Name | Application | |
| DPAB-JXL23170 | Rabbit Anti-CHO HCP polyclonal antibody | WB | Inquiry |
| DPAB-JXL23235 | Goat Anti-E. coli expression strains HCP polyclonal antibody | IA | Inquiry |
| DPAB-JXL23236 | Goat Anti-E. coli clonal strains HCP polyclonal antibody | IA | Inquiry |
| DPAB-JXL23237 | Goat Anti-CHO HCP polyclonal antibody | IA | Inquiry |
| DEIABL494 | S.cerevisiae HCP ELISA kit | Quantitative | Inquiry |
| DEIABL482 | HEK 293 HCP ELISA Kit | Quantitative | Inquiry |
| DEIABL495 | SF9 HCP ELISA Kit | Quantitative | Inquiry |
| DEIASL170 | SF9 Insect Cell HCP ELISA Kit | Quantitative | Inquiry |
| View More |