Filter By Product Search for
IL6
 Loading...
Loading...
IL6 Products
IL6 Full Name
Interleukin 6
IL6 Introduction
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine that plays a significant role in the immune system and various physiological processes. Produced by a variety of cells, including immune cells, IL-6 acts as a key mediator of inflammation and immune responses. It stimulates the production of acute-phase proteins, recruits immune cells to sites of inflammation, and regulates the differentiation and activation of immune cells. IL-6 also has important functions outside of the immune system. It is involved in tissue regeneration and repair, promoting the proliferation and survival of various cell types. Furthermore, IL-6 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and certain viral infections. Its dysregulation can contribute to chronic inflammation and immune dysfunction.
The signaling of IL-6 is mediated through a receptor complex consisting of the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and glycoprotein 130 (gp130). Upon binding to its receptor, IL-6 triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling pathways, mainly including the JAK-STAT pathway and MAPK pathway. These pathways regulate gene expression, leading to the activation of immune cells, the production of inflammatory mediators, and the modulation of cellular responses. The balance between pro-inflammatory and regulatory effects of IL-6 is crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis. Dysregulated IL-6 signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases, and targeting IL-6 or its receptors has emerged as a therapeutic strategy for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and cytokine storm syndrome.
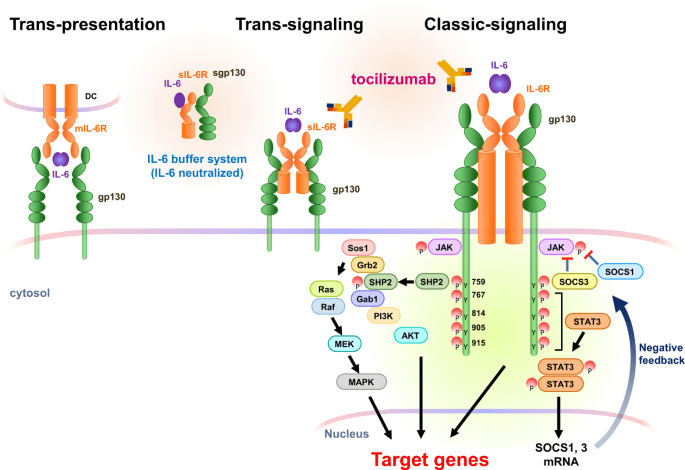 Figure 1. Three modes of IL-6R signaling and their associated intracellular pathways.
Figure 1. Three modes of IL-6R signaling and their associated intracellular pathways.
(Source: Kang, S. et al., 2020)
Therapeutic interventions targeting IL-6 have shown promise in the treatment of certain diseases. Monoclonal antibodies that block IL-6 or IL-6R, such as tocilizumab, have been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Castleman's disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. These antibodies disrupt IL-6 signaling, dampen inflammation, and modulate immune responses. Moreover, anti-IL-6 therapy was also evaluated for cancer treatment. However, the use of IL-6-targeted therapies requires careful consideration, as IL-6 plays crucial roles in immune defense and tissue homeostasis. Ongoing research aims to further elucidate the complex functions of IL-6 and develop targeted therapies that can effectively modulate its activity in specific disease contexts while preserving its beneficial effects.
Alternate Names for IL6
IL6
interleukin 6
HGF
HSF
BSF2
IL-6
IFNB2
interleukin-6
CDF
BSF-2
IFN-beta-2
interferon beta-2
interleukin BSF-2
interferon
beta 2
hybridoma growth factor
CTL differentiation factor
B-cell stimulatory factor 2
B-cell differentiation factor
PF-04236921
- Cancer Cancer and Inflammation Inflammatory Mediators
- Cancer Cancer and Inflammation Ion Channels and Regulators
- Cancer Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) MDSC Cytokines and Growth Factors
- Cell Biology The Reticuloendothelial System The Reticuloendothelial System
- Cardiovascular Atherosclerosis Ion Channels and Regulators
- Cardiovascular Extracellular Matrix and Cardiovascular Inflammatory Mediators
Increased interleukin-6 is associated with long COVID-19
COVID-19 may lead to persistent, sequelae and other clinical complications that last weeks to months and eventually evolve into long-term COVID-19. Previous studies have shown that IL-6 is associated with COVID-19. However, the correlation between IL-6 and long-term COVID-19 is unknown. Researchers designed a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis to assess the relationship between IL-6 levels and long-term COVID-19.
The analysis included 22 studies published before September 2022. The results showed that IL-6 levels were higher in patients with long COVID-19 compared to healthy individuals and those with non-postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. This suggests that IL-6 could be a useful marker for predicting or indicating the early stage of long COVID-19. The new study provides valuable insights into the correlation between elevated IL-6 and long COVID-19.
- 1. Kang S, Kishimoto T. Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms. Experimental & Molecular Medicine. 2021, Jul, 53(7):1116-1123
2. Yin J X, et al. Increased interleukin-6 is associated with long COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 2023, 12(1): 43.
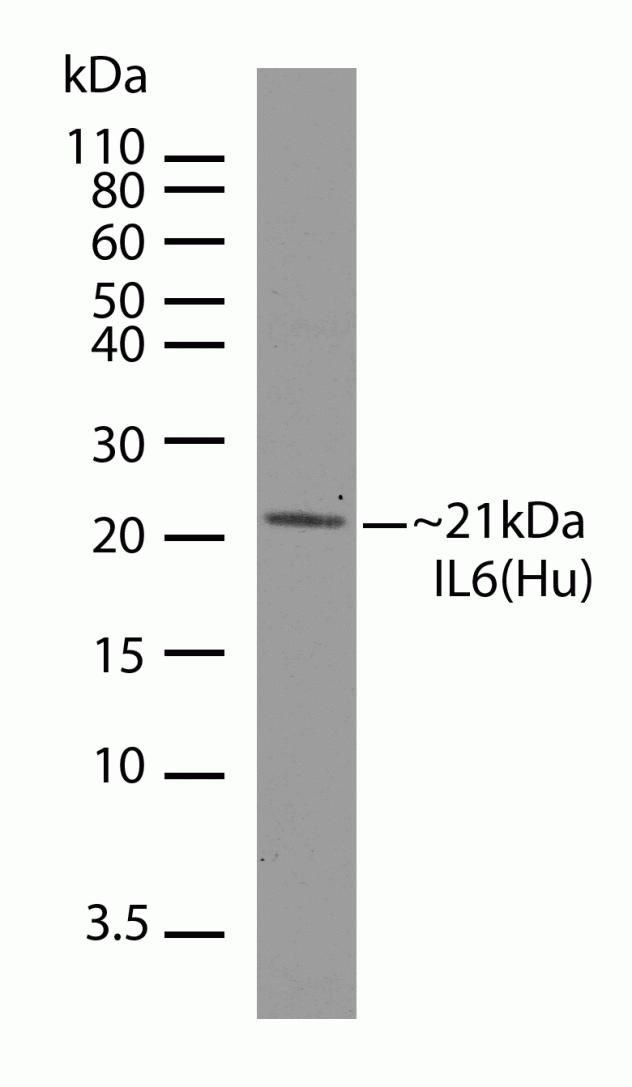
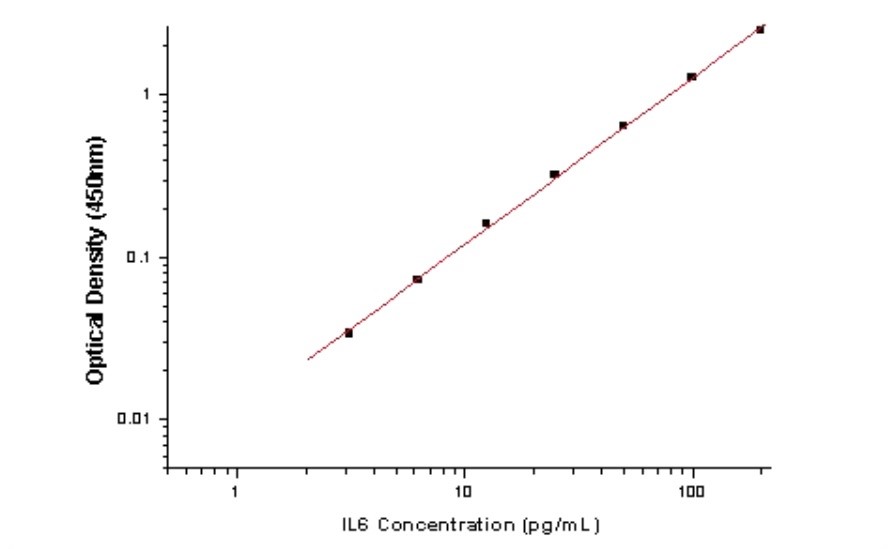
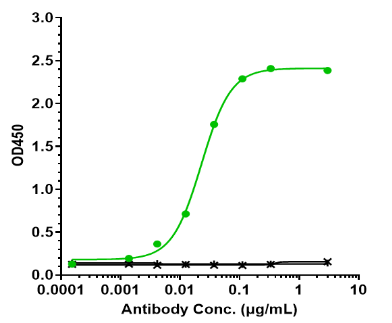

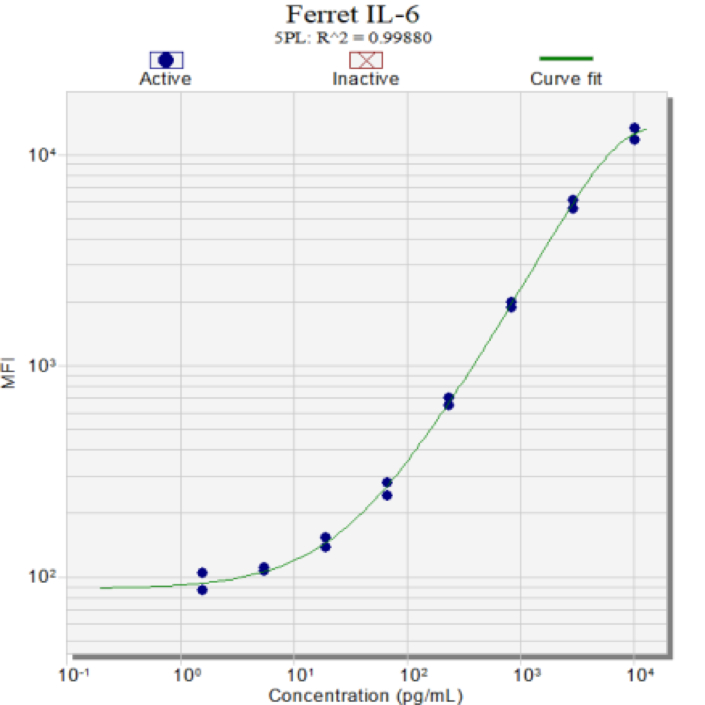
 Cell Signaling
Cell Signaling