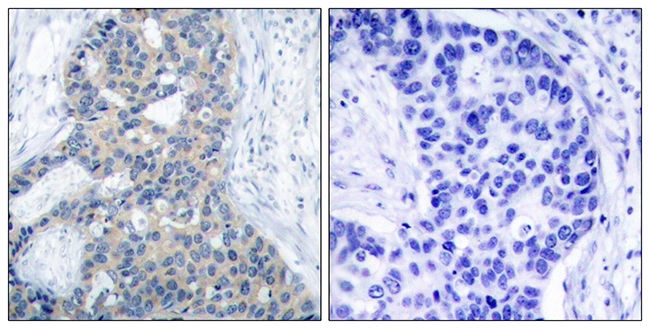
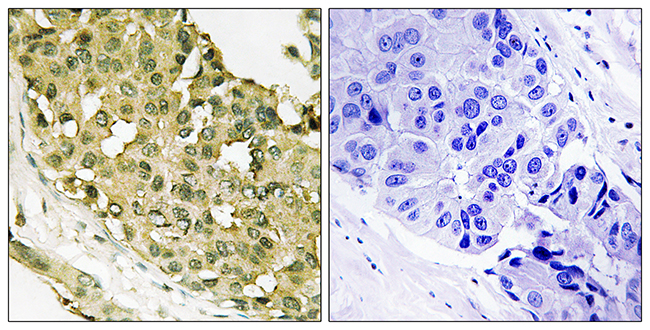
STMN1 upregulation mediates hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic stellate cell crosstalk to aggravate cancer by triggering the MET pathway
CANCER SCIENCE
Authors: Zhang, Rui; Gao, Xiaomei; Zuo, Jieliang; Hu, Beiyuan; Yang, Jimeng; Zhaol, Jing; Chen, Jinhong
Abstract
STMN1 has been regarded as an oncogene and its upregulation is closely associated with malignant behavior and poor prognosis in multiple cancers. However, the detailed functions and underlying mechanisms of STMN1 are still largely unknown in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. Herein, we analyzed STMN1 expression and the related clinical significance in HCC by using well-established Protein Atlas, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) cancer databases. Analysis indicated that STMN1 was highly expressed in HCC and closely associated with vascular invasion, higher histological grade, advanced clinical grade and shorter survival time in HCC patients. Overexpressing and silencing STMN1 in HCC cell lines showed that STMN1 could regulate cell proliferation, migration, drug resistance, cancer stem cell properties in vitro as well as tumor growth in vivo. Further experiments showed that STMN1 mediated intricate crosstalk between HCC and hepatic stellate cells (HSC) by triggering the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/ MET signal pathway. When HSC were cocultured with HCC cells, HSC secreted more HGF to stimulate the expression of STMN1 in HCC cells. Mutually, STMN1 upregulation in HCC cells facilitated HSC activation to acquire cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) features. The MET inhibitor crizotinib significantly blocked this crosstalk and slowed tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, our findings shed new insight on STMN1 function, and suggest that STMN1 may be used as a potential marker to identify patients who may benefit from MET inhibitor treatment.
Systemic Delivery of MicroRNA-101 Potently Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vivo by Repressing Multiple Targets
PLOS GENETICS
Authors: Zheng, Fang; Liao, Yi-Ji; Cai, Mu-Yan; Liu, Tian-Hao; Chen, Shu-Peng; Wu, Pei-Hong; Wu, Long; Bian, Xiu-Wu; Guan, Xin-Yuan; Zeng, Yi-Xin; Yuan, Yun-Fei; Kung, Hsiang-Fu; Xie, Dan
Abstract
Targeted therapy based on adjustment of microRNA (miRNA)s activity takes great promise due to the ability of these small RNAs to modulate cellular behavior. However, the efficacy of miR-101 replacement therapy to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. In the current study, we first observed that plasma levels of miR-101 were significantly lower in distant metastatic HCC patients than in HCCs without distant metastasis, and down-regulation of plasma miR-101 predicted a worse disease-free survival (DFS, P<0.05). In an animal model of HCC, we demonstrated that systemic delivery of lentivirus-mediated miR-101 abrogated HCC growth in the liver, intrahepatic metastasis and distant metastasis to the lung and to the mediastinum, resulting in a dramatic suppression of HCC development and metastasis in mice without toxicity and extending life expectancy. Furthermore, enforced overexpression of miR-101 in HCC cells not only decreased EZH2, COX2 and STMN1, but also directly down-regulated a novel target ROCK2, inhibited Rho/Rac GTPase activation, and blocked HCC cells epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis, inducing a strong abrogation of HCC tumorigenesis and aggressiveness both in vitro and in vivo. These results provide proof-of-concept support for systemic delivery of lentivirus-mediated miR-101 as a powerful anti-HCC therapeutic modality by repressing multiple molecular targets.
![]()