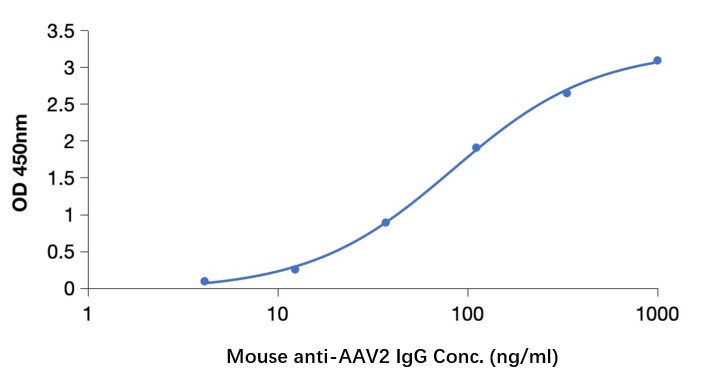
GTCDxᵀᴹ Anti-AAV2 antibody ELISA Kit
Regulatory status: For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedures.
| No. | Components | Size | Storage Conditions |
| 1 | AAV2 Capsid Coated Microtiter Plate | 12 × 8 wells | 2-8°C |
| 2 | Negative Control, ready to use | 1 × 1 ml | 2-8°C |
| 3 | Anti-AAV2 Positive Control, ready to use | 1 × 1 ml | 2-8°C |
| 4 | Cut-off Control, ready to use | 1 × 1 ml | 2-8°C |
| 5 | Anti-human IgG Conjugate, ready to use | 1 × 12 ml | 2-8°C |
| 6 | Sample Diluent, ready to use | 1 × 50 ml | 2-8°C |
| 7 | Wash Buffer, 20 × concentrate | 1 × 50 ml | 2-8°C |
| 8 | TMB Substrate, ready to use | 2 × 6 ml | 2-8°C |
| 9 | Stop Solution, ready to use | 1 × 7 ml | 2-8°C |
| 10 | Instruction Manual | 1 |
2. All reagents and wash buffer should be used within 12 months from manufacturing date.
3. Before using, bring all components to room temperature (18-25°C). Upon assay completion ensure all components of the kit are returned to appropriate storage conditions.
4. The Substrate is light-sensitive and should be protected from direct sunlight or UV sources.
Non-scaled Venn diagram depicting the relationship between total (tAb) and specific confirmed total antibodies in samples. The results are highly consistent, indicating that ELISA has high accuracy in detecting AAV antibodies.

Recombinant vectors based on AAV2 (rAAV2) have been, or are currently being, used in a number of Phase I/II clinical trials, and thus far, no serious adverse events, much less cancer of any type have ever been observed or reported. Furthermore, the use of rAAV2 vectors has led to clinical efficacy in the potential gene therapy of at least three human diseases: Leber's congenital amaurosis (LCA), aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency (AADC) and choroideremia.
One of the major challenges in AAV-based gene therapy is the presence of circulating anti-AAV neutralizing antibodies, which can pre-exist in patients and may prevent successful gene transfer. High levels of circulating anti-AAV neutralizing antibodies can develop after a single administration of gene therapy and can prevent successful gene transfer in patients.
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Applications | Host Species | Datasheet | Price | Add to Basket |
|---|
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are small, icosahedral viruses that have become one of the most important gene vectors in the field of gene therapy due to their long-term expression, low toxicity, low immunogenicity, and high tissue specificity. In particular, adeno-associated virus 2 (AAV) has been demonstrated to be one such promising vector in gene therapy as it exhibits several desirable characteristics, including non-pathogenicity based on wild-type (wt) virus, the ability to infect dividing and non-dividing cells, and the establishment of long-term expression of heterologous genes by recombinant AAV. At present, recombinant AAV (rAAV) vectors are being evaluated in human clinical trials for the treatment of various diseases such as type B hemophilia and cystic fibrosis.
In gene therapy and vector-based research, it is crucial to monitor and evaluate the immune response against AAV2. Upon administration of AAV2 vectors, the host immune system may mount an immune response by producing antibodies against AAV2 capsid proteins. These antibodies can potentially neutralize the viral vectors and limit their effectiveness in delivering therapeutic genes. Therefore, the detection and quantification of anti-AAV2 antibodies are essential for assessing the immunogenicity of AAV2 vectors, evaluating their potential efficacy, and monitoring patient immune responses in clinical trials. With versatility, high-throughput capabilities, and quantitative results, the Anti AAV2 Antibody ELISA Kit (DEIASL347) provides a valuable tool for evaluating immune responses against AAV2 virus vectors in gene therapy and research applications.
Anti-AAV2 antibody ELISA
Anti-Adeno-associated virus type 2 antibody ELISA
Anti-Adeno-associated virus 2 antibody ELISA
Anti-Adeno-associated virus type 2 antibody ELISA Kit
Anti-Adeno-associated virus 2 antibody ELISA Kit
Q: How did you determine the cut-off point?
A: We used our kit and a confirmed assay method in the literature to determine the cut-off
Q: Which samples (sera, plasma, etc.) did you use to determine the cut-off?
A: Serum
Q: How did you determine the reference limit? Was it according to CLSI EP28-A3c guidelines?
A: Our method is similar to CLSI EP28-A3c guidelines, both of which use statistical methods. But we don't refer to this file
Q: Do we have to pre-dilute our samples?
A: Dilution: 1:50
Q: Are the negative / positive / cut-off controls serum, plasma or buffer?
A: All three of our controls contained antibody buffers and no serum components
Q: How many samples did you use?
A: AAV2 (76 samples)
Q: We wanted to compare anti-monkey IgG and anti-human IgG in an ELISA kit. Will the result matter?
A: Our results are derived from human serums. If the monkey serum is measured or the anti-monkey IgG secondary antibody is replaced, the result should be inaccurate. Because we ignored the background effect brought by human serum after optimizing the system. After replacing the serum/secondary antibody, it is not sure what will be affected (such as secondary antibody specificity, background value increase, etc.). Therefore, if the calculation is performed directly, it should be possible that the result is inaccurate.
Q: What is the blank well or how do you blank ? I don't see blank well in your design. We may need to recalculate the raw data.
A: Our kit does not set blank (neither does MBL). After system optimization, the calculation can be performed without considering the blank, and the results will not be affected by the blank of different serums.
Q: Which butter of your anti-human IgG? In sample diluent buffer or other solution? We want to compare anti-monkey IgG with your antihuman IgG in your ELISA kit.
A: The buffer is ABS, and there is no detailed composition of the buffer (it can be said to be know-how?). It is known that it is a PBS matrix, containing preservatives and protein components.
Improved Method of Recombinant AAV2 Delivery for Systemic Targeted Gene Therapy
Molecular Therapy
Authors: Mah C, Fraites T J, Zolotukhin I, et al.
AAV2-mediated in vivo immune gene therapy of solid tumours
Genetic Vaccines and Therapy
Authors: Collins S A, Buhles A, Scallan M F, et al.
Methods: Immune-competent Balb/C or C57 mice bearing subcutaneous JBS fibrosarcoma or Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumour xenografts respectively were treated by intra-tumoural administration of AAV2 vector encoding the immune up-regulating cytokine granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and the co-stimulatory molecule B7-1 to subcutaneous tumours, either alone or in combination with intra-muscular (IM) delivery of AAV2 vector encoding Nk4 14 days prior to tumour induction. Tumour growth and survival was monitored for all animals. Cured animals were re-challenged with tumourigenic doses of the original tumour type. In vivo cytotoxicity assays were used to investigate establishment of cell-mediated responses in treated animals.
Results: AAV2-mediated GM-CSF, B7-1 treatment resulted in a significant reduction in tumour growth and an increase in survival in both tumour models. Cured animals were resistant to re-challenge, and induction of T cell mediated anti-tumour responses were demonstrated. Adoptive transfer of splenocytes to naïve animals prevented tumour establishment. Systemic production of Nk4 induced by intra-muscular (IM) delivery of Nk4 significantly reduced subcutaneous tumour growth. However, combination of Nk4 treatment with GM-CSF, B7-1 therapy reduced the efficacy of the immune therapy.
Conclusions: Overall, this study demonstrates the potential for in vivo AAV2 mediated immune gene therapy, and provides data on the inter-relationship between tumour vasculature and immune cell recruitment.
- AAV Antibodies and Titration ELISA
- Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Antigens
- GTCDxᵀᴹ Anti-AAV Antibody ELISA Kits
Invoice / Purchase Order
Credit card
![]()